Select one production and evaluate it in relation to ONE of the following media concepts: AUDIENCE
Today we ask: what do we understand by the meaning of audience?
For A2 you will need to know and understand some of the theories about Media Audiences.
We have previously discussed frameworks for audience theory:- Media Effects or hypodermic syringe model;
- Two-step flow model;
- Uses and Gratifications model;
- Active audiences/ participatory culture, like citizen journalism, interactivity, blogs YouTube, FaceBook;
- Reception theory [preferred, negociated & oppositional readings] which you can revise here.)
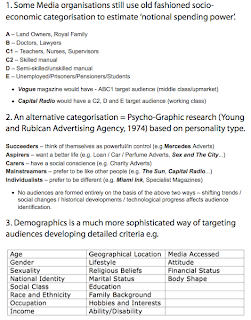
- audience profiling, such as socioeconomics,demographics, psychographics
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs
- mainstream / niche audiences
- target audiences
- viewing figures BARB, RADAR
We also know that audience segmentation has changed because of digital transmission
- proliferation of channels
- internet allows producers to distribute without institutions: blogs, YouTube
- increase in platforms
- viewing on demand
- Stuart Hall The Birmingham School; Cultural Studies; hegemony: the winning of consent to unequal class relations. Reception analysis is an active audience theory that looks at how audiences interact with a media text taking into account their ‘situated culture’ – this is their daily life. The theory suggests that social and daily experiences can affect the way an audience reads a media text and reacts to it. This theory about how audiences read a text was put forward by Professor Stuart Hall‘The Television Discourse - Encoding/Decoding’ in 1974 with later research by in David Morley in 1980 and Charlotte Brunsden. He suggests that an audience has a significant role in the process of reading a text, and this can be discussed in three different ways: the dominant or preferred reading, the negociated reading and the oppositional reading.
- Henry Jenkins and participatory culture Textual Poachers
- Matt Hills negative fan stereotypes and positive fan injunctions
No comments:
Post a Comment